Wednesday, 28 September 2016
Character Coding Exam questions
Question 1.
a) How many characters can be represented using ASCII? 128
b) How would the character E be represented using 7 bits? 1000101
c) Characters are transmitted using an e-bit code that includes a parity bit in the most significant bit?
D- 01000100
E- 11000101
H- 01001000
d) Parity works by either using odd or even parity. If there is an odd number of 1s in the end binary parity bit will be a 0. There are 1 bit and 3 bit parity. 1 bit is most common because it requires less data to be sent and is therefore cheaper to implement. At the receiving end, the code can be checked to see whether the number is still odd or even.
Question 2.
a) 53- 0110101
b)0110110
c) 9=57 0=48 difference is 9
d)1
e)3
f)The advantages of majority vote over parity bits is that the majority vote can repair the errors because the data is being sent multiple times where a parity bit can only detect that there is an error.
Character Codes Passport questions
1. What 3 different character systems exist and how many characters does each hold?
Ascii-128 characters, Extended Ascii-256 characters, Unicode-65,536 characters.
2. What are the decimal code equivalent of some letters in the alphabet? what are the Binary versions? a is 97 or 1100001. e is 101 1100101.
3. What are the differences with character codes of capital and lower case letter? They have a decimal difference of 32. The 32 bit is different. 0 is capital 1 is lower case.
4. What is meant by a parity bit? How does Parity work? what different parity systems are there? Parity bit is an extra bit on the end of the information to make sure it is correct and has not been changed. Parity works by either using odd or even parity. so if there is an odd or even number of 1 the end parity bit will be a 1 or 0. There are 1 bit and 3 bit parity. ! bit is most common because it requires less data to be sent and is therefore cheaper to implement.
5. What is meant by a check digit? How does this work? A check digit works by using the rest of the numbers then multiplying them and adding them. Then the check digit is the number between the total and the total rounded up to the nearest 10.
6. What is majority vote? How does it work? Majority vote is when the computer decides whether info is correct by what the majority of that bit is. so the info is sent 3 times and the majority of the 1s or 0s for that bit is what the computer assumes correct.
Ascii-128 characters, Extended Ascii-256 characters, Unicode-65,536 characters.
2. What are the decimal code equivalent of some letters in the alphabet? what are the Binary versions? a is 97 or 1100001. e is 101 1100101.
3. What are the differences with character codes of capital and lower case letter? They have a decimal difference of 32. The 32 bit is different. 0 is capital 1 is lower case.
4. What is meant by a parity bit? How does Parity work? what different parity systems are there? Parity bit is an extra bit on the end of the information to make sure it is correct and has not been changed. Parity works by either using odd or even parity. so if there is an odd or even number of 1 the end parity bit will be a 1 or 0. There are 1 bit and 3 bit parity. ! bit is most common because it requires less data to be sent and is therefore cheaper to implement.
5. What is meant by a check digit? How does this work? A check digit works by using the rest of the numbers then multiplying them and adding them. Then the check digit is the number between the total and the total rounded up to the nearest 10.
6. What is majority vote? How does it work? Majority vote is when the computer decides whether info is correct by what the majority of that bit is. so the info is sent 3 times and the majority of the 1s or 0s for that bit is what the computer assumes correct.
Tuesday, 27 September 2016
ISBN Check digit
ISBN Check digit
A ISBN is used to make sure a book code is legal. It is worked out and the check digit is the final digit of the 13 digit combination that makes up the ISBN Code. Here I have an example of my Excel spread sheet that can be used to easily find the check digit and 13 digit code from the first 12 digits. simply input the digits in and it produces the full code at the bottom in orange. You will notice the check digit is in the 13th number column.
Monday, 26 September 2016
Character sets
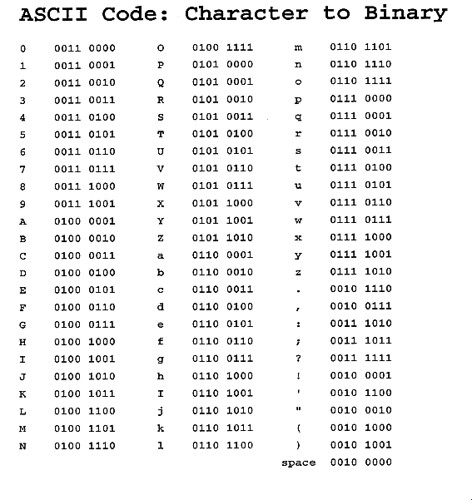
Tasks-Character Coding
1. A) What does ASCII stand for?
American standard communication information interchange
American standard communication information interchange
B) What is it used
for?
To create a more universal form of coding information mapping the same characters to certain binary numbers.
To create a more universal form of coding information mapping the same characters to certain binary numbers.
2. A) How many characters can you have with 7 bit ASCII?
128
B) What is 8 bit ASCII known as? How many characters can you
have with this?
You can have 256 characters
You can have 256 characters
3. What is the ASCII denary character codes for A, C, E?
A=65 C=67 E=69
A=65 C=67 E=69
4. How do we represent all of the characters from for e.g.
Arabic / China ?
We use character set called Unicode.
We use character set called Unicode.
5. What is meant by Parity?
It is a technique that checks whether data has been lost or written over when it is moved from one place in storage to another or when it is transmitted between computers.
It is a technique that checks whether data has been lost or written over when it is moved from one place in storage to another or when it is transmitted between computers.
6. Write your name in ASCII (Binary)
1001010 , 1100001 , 11001101 , 1100101 , 1110011
1001010 , 1100001 , 11001101 , 1100101 , 1110011
J a m e s
7. What is the letter from the ASCII code 80? P
8. What is the difference in bit pattern from a capital A to
a lower case a?
The second most important bit determines if it is a capital or lower case. 0=A , 1=a.
The second most important bit determines if it is a capital or lower case. 0=A , 1=a.
9. What is Character Set?
A set of symbols
used to convey information.
Wednesday, 21 September 2016
Variables and data types
| Data type | Description | Sample data |
|---|---|---|
| INTEGER | Stores positive or negative whole numbers | 17 |
| REAL | Stores numbers that contain decimal places/values and can also store integers | 17.65 |
| CHARACTER | Stores a single character which can be a letter, number or symbol | $ |
| STRING | Stores alphanumeric combinations and text. String is really a group of characters stored together as one. Numbers to be used for calculations should not be stored as string data even though they can be. They should be stored as INTEGER or REAL | Batman |
| BOOLEAN | Stores True or False only. This is sometimes taught as 1 or 0 only where 1 is true and 0 false | True |
In a program, data values can be constant or variable. If values are variable they can be changed by the program and the user. When a program is run, the data values are held in memory whilst they are being worked on.
Constants: Data values that stay the same every time a program is executed are known as constants. Constants are not expected to change.
Variables: are data values that can change when the user is asked a question, for example, their age. Variables may change during program execution.
A variable is a memory location. It has a name that is associated with that location. The memory location is used to hold data. The key difference when comparing a constant to a variable is that the value associated with a variable name may change during program execution. For example 'highScore' would need to be variable to change throughout a game.
Tuesday, 13 September 2016
Franklin start milestone
Franklin Start Milestone
Six
Famous pioneers of Computer Science:
•Tim
Berners-Lee.
•Leonard
Kleinrock.
•Konrad
Zuse.
•Steve
Wozniak.
•Ada
•John
Atanasoff.
Milestones of development in computing history:
1800s- First works and notes on computer programs.
This paved the way for modern computer programs and laid the foundation for
computer programming.
First electronic digital computer in the 1930s.
World's first programmable computer. The functional program-controlled Turing-complete Z3 became operational in May 1941.
The first message on the ARPANET was sent by
UCLA student programmer Charley
Kline, at 10:30 p.m, on October 29, 1969. The Advanced
Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) was an early packet
switching network and the first network to implement the protocol
suite TCP/IP. Both technologies became the technical foundation of
the Internet. ARPANET was initially funded by the Advanced Research
Projects Agency (ARPA) of the United States Department of Defense.
John Vincent Atanasoff (October 4, 1903 – June 15, 1995) was an American physicist and inventor. He is known for being credited with inventing the first electronic digital computer.
Konrad Zuse (22 June 1910 – 18 December 1995) was a German civil engineer, inventor and computer pioneer. His greatest achievement was the world's first programmable computer. The functional program-controlled Turing-complete Z3 became operational in May 1941. Thanks to this machine and its predecessors, the Z1 and the Z2 Zuse has often been regarded as the inventor of the modern computer.
Due
to World War II, Zuse's work went largely unnoticed in the United Kingdom and the United States US
Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee OM KBE FRS FREng FRSA FBCS (born 8 June 1955), also known as TimBL, is an English computer scientist, best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web.
He made a
proposal for an information management system in March 1989, and he
implemented the first successful communication between a Hypertext
Transfer Protocol (HTTP) client and server via the Internet sometime
around mid-November of that same year.
Berners-Lee
is the director of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), which
oversees the continued development of the Web. He is also the founder of
the World Wide Web Foundation, and is a senior researcher and holder of
the founders chair at the MIT Computer Science and Artificial
Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL). In 2004, Berners-Lee
was knighted by Queen Elizabeth II for his pioneering work.
In April 2009, he was elected a foreign associate of the United States
National Academy of Sciences. Named in Time magazine's list of
the 100 Most Important People of the 20th century, Berners-Lee has
received a number of other accolades for his invention.
Stephen Gary "Steve" Wozniak (August 11, 1950) nicknamed "Woz", and sometimes The Wonderful Wizard of Woz, is an American inventor, electronics engineer, programmer, and technology entrepreneur who co-founded Apple Inc. He is known as a pioneer of the personal computer revolution of the 1970s and 1980s, along with Apple co-founder Steve Jobs.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
